This DIY smart chicken coop features AI-based predator detection
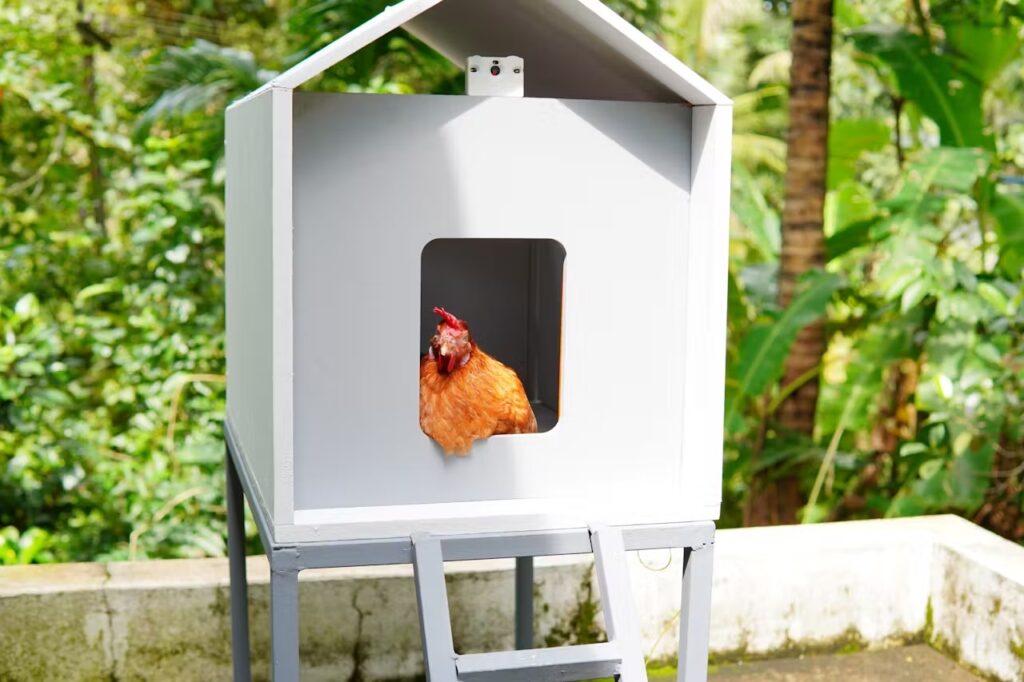

Raising chickens can be a very rewarding endeavor, as they can provide fresh daily eggs and help get rid of pests in the yard. But, like all animals, they require care. Most importantly, you’ll need to ensure that they have regular food and water, and you’ll need to protect them from predators like coyotes, foxes, and cats. To ease the workload, you may want to consider building Coders Cafe’s DIY smart chicken coop that features AI-based predator detection.
The purpose of a coop, aside from being a comfy place for chickens to roost, is to provide protection from weather and predators. This design is pretty small and is probably only suitable for one or two chickens, but the concepts can be applied to larger coops. It provides a few very useful features: remote or automated feeding, remote or automated door operation, and predator detection with remote notifications. You’ll never have to worry that you forgot to feed the chickens or that you left the door open, and you can respond immediately if you get a notification about a predator.
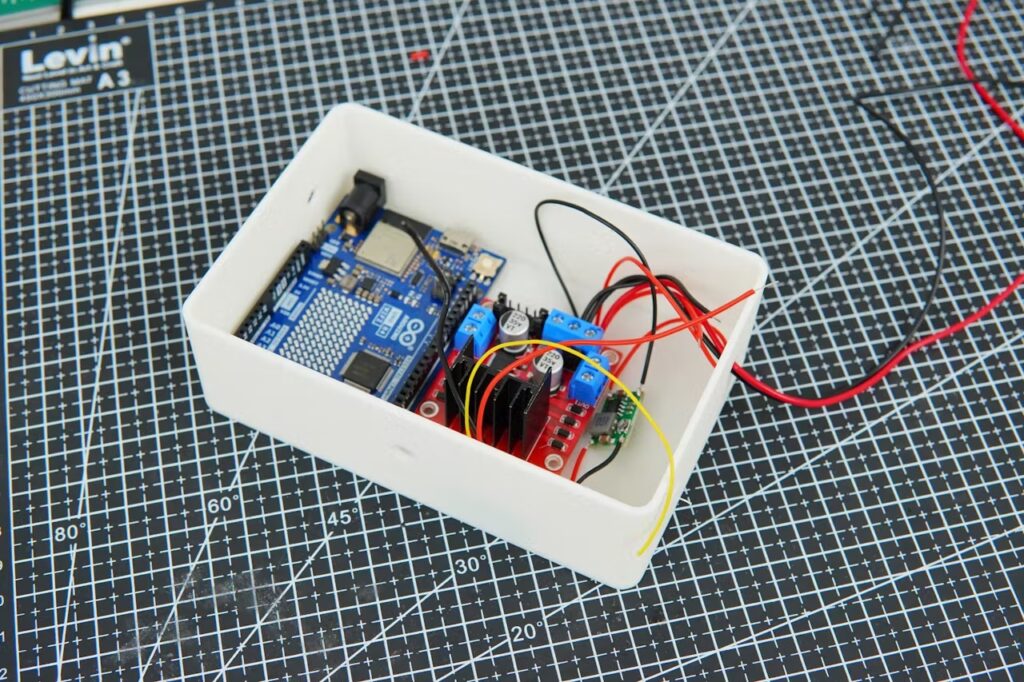
An Arduino UNO R4 WiFi board oversees those features, operating the door and dispensing food using simple motor-driven mechanisms. A companion app lets the user set an automated door and food schedule, or perform those actions with the tap of the button. A Twilio app integration enables SMS alerts.
The predator-detecting magic works thanks to DFRobot’s HuskyLens AI camera sensor. Users can train that to recognize specific predators and then it will tell the Arduino if it sees one. That communication occurs over I2C and is easy to setup, removing all of the difficulty of implementing AI.
The post This DIY smart chicken coop features AI-based predator detection appeared first on Arduino Blog.